what are the 6 types of anxiety disorders
Generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, specific phobias, obsessive-compulsive disorder, and post-traumatic stress disorder constitute the six types of anxiety disorders. These disorders cause excessive fear or worry, often leading to avoidance behaviors and impairment in daily functioning.
Understanding the different types of anxiety disorders is crucial for identifying symptoms and seeking appropriate treatment. Each type of anxiety disorder has unique characteristics and may require specialized interventions. By recognizing the specific features of each disorder, individuals and healthcare professionals can address and manage anxiety effectively.
Let’s explore the distinctions and implications of these anxiety conditions to better comprehend their impact on mental health and well-being.
Definition Of Anxiety Disorders
Anxiety disorders are a group of mental health conditions characterized by overwhelming feelings of fear and worry. These disorders can significantly impair a person’s ability to function in daily life, causing distress and impacting their overall well-being. There are six main types of anxiety disorders, each with its own specific symptoms and triggers. Understanding these different types can help individuals recognize and seek appropriate treatment for their specific anxiety-related challenges.
What Is Anxiety?
Anxiety, in general, is a natural response to stress or a perceived threat. While experiencing anxiety is a normal part of life, excessive and persistent feelings of anxiety can develop into an anxiety disorder, leading to significant distress and impairment.
Difference Between Anxiety And Anxiety Disorders
It’s essential to differentiate between normal feelings of anxiety and an anxiety disorder. While occasional anxiety is a common reaction to stressful situations, anxiety disorders involve intense and chronic feelings of unease that can interfere with daily activities, including work, school, and relationships. This crucial distinction between anxiety and anxiety disorders helps individuals recognize when their anxiety may require professional intervention for effective management and treatment.
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) is a common mental health condition characterized by persistent, excessive, and uncontrollable worry about various life events or activities. People with GAD often anticipate disaster and are overly concerned about money, health, family, work, or other issues, even when there is little or no reason to worry. This chronic worrying can significantly impact their daily life, causing emotional distress and interfering with their ability to function normally.
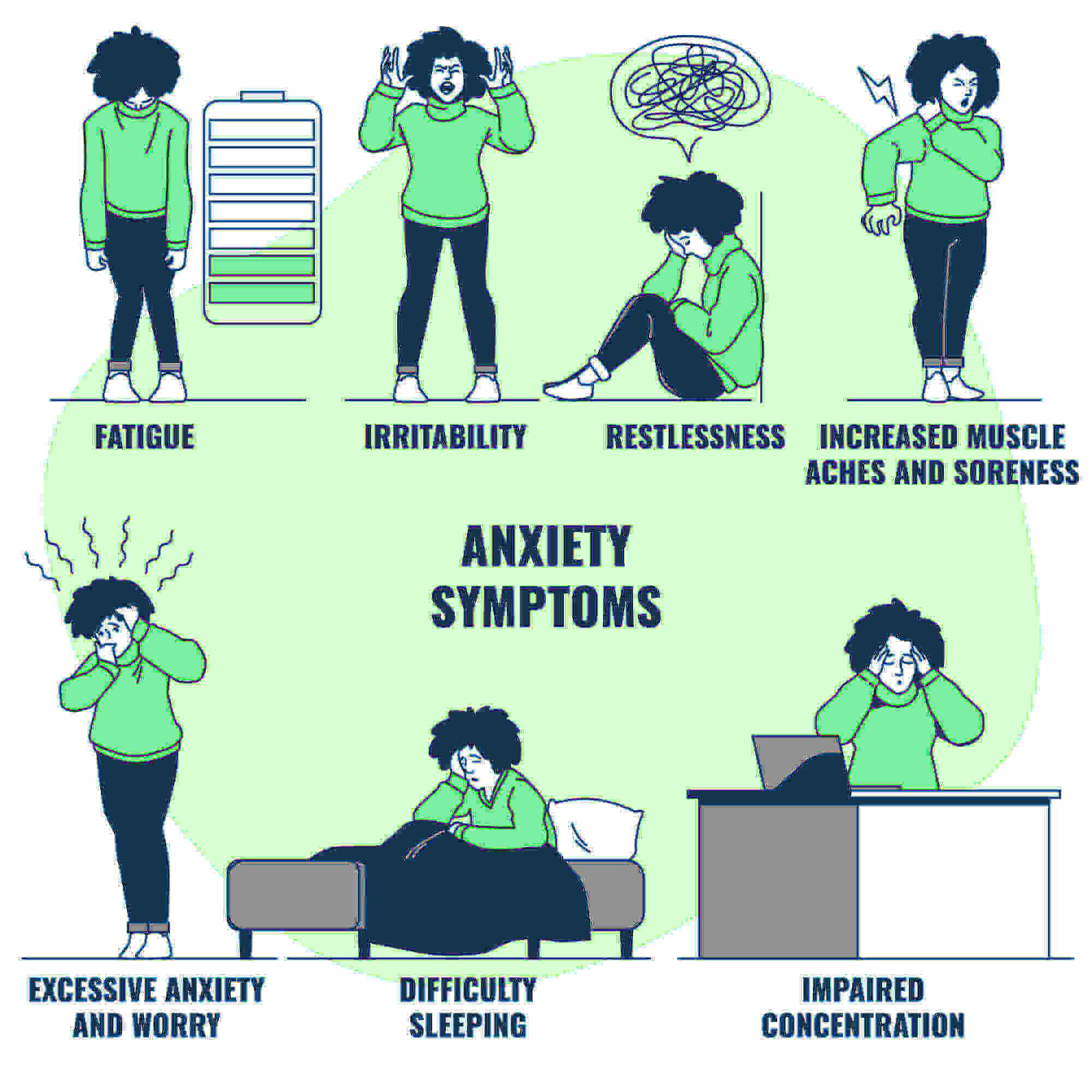
Symptoms And Characteristics
- Intense concern and anxiety regarding a broad spectrum of events or activities.
- Difficulty controlling the worry
- Restlessness or feeling on edge
- Difficulty concentrating or mind going blank
- Irritability
- Muscle tension
- Disruptions in sleep, such as challenges in initiating or maintaining sleep.
Treatment Options
Treatment for GAD often involves a combination of therapy and medication. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is a common approach that helps individuals understand and change their thought patterns and behaviors related to anxiety. Medications such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) or serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) may also be prescribed to alleviate symptoms of GAD.
Panic Disorder
Panic disorder is characterized by sudden and repeated panic attacks which are accompanied by intense fear and apprehension. The symptoms of panic attacks can often mimic those of a heart attack, leading to further distress for the individual. These episodes can occur without any warning and can be immensely debilitating, causing individuals to limit their activities or even avoid certain places or situations to prevent a recurrence.
Differentiating Panic Attacks And Panic Disorder
While panic attacks can be a component of panic disorder, it’s important to note the distinction between the two. Panic attacks are unexpected and can occur in various circumstances, while panic disorder involves recurrent and unexpected panic attacks along with a persistent fear of having more attacks.
Coping Strategies
Individuals with panic disorder can implement several coping strategies to better manage their symptoms:
- Practice deep breathing and relaxation techniques to reduce the intensity of a panic attack
- Engage in regular physical activity to alleviate stress and anxiety
- Seek therapy or counseling to address underlying triggers and learn effective coping mechanisms
- Utilize mindfulness and meditation to promote emotional resilience
- Educate oneself about panic disorder to gain better insight and understanding of the condition
Social Anxiety Disorder
Social anxiety disorder, also known as social phobia, is characterized by an overwhelming fear of social situations. Individuals with this condition may experience intense anxiety and self-consciousness in everyday social interactions, leading to avoidance of such situations. This can significantly impact their personal and professional lives, making it important to address and manage this disorder effectively.
Impact On Daily Life
The daily life of an individual can be significantly affected by social anxiety disorder. It can lead to avoidance of social interactions, which may affect personal relationships, career opportunities, and overall well-being. The fear of judgment or embarrassment can cause significant distress, leading to feelings of isolation and loneliness. The impact of social anxiety disorder can extend to various aspects of life, making it essential to seek treatment and support in managing these challenges.
Behavioral Therapies
Behavioral therapies play a crucial role in addressing social anxiety disorder. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is one of the most effective approaches, helping individuals identify and challenge negative thought patterns and behaviors related to social anxiety. Exposure therapy, a form of CBT, involves gradually exposing individuals to feared social situations, allowing them to develop coping strategies and reduce anxiety. These behavioral therapies aim to empower individuals to overcome social anxiety and regain control over their social interactions and daily life.
Specific Phobias
Specific phobias are a type of anxiety disorder characterized by excessive and irrational fear of specific objects or situations. These phobias can cause significant distress and impairment in daily life. While most people may have some level of fear or discomfort towards certain things, specific phobias are more intense and can interfere with a person’s ability to function normally. Understanding common specific phobias and effective treatments like exposure therapy can provide valuable insights into managing these anxiety disorders.
Common Phobias
Specific phobias can be associated with various objects, animals, activities, or situations. Some common specific phobias include:
- Fear of heights (acrophobia)
- Fear of spiders (arachnophobia)
- Fear of flying (aviophobia)
- Fear of enclosed spaces (claustrophobia)
- Fear of needles or injections (trypanophobia)
Exposure Therapy
This form of therapy is often used to treat specific phobias. It involves gradually exposing individuals to the object or situation they fear in a controlled and safe environment. This exposure is designed to help individuals confront and manage their fear, ultimately reducing their anxiety response. Over time, repeated exposure can lead to desensitization and a reduction in phobia-related symptoms, allowing individuals to regain control over their lives.
Obsessive-compulsive Disorder (ocd)
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) is a type of anxiety disorder characterized by persistent, unwanted thoughts or obsessions, and repetitive behaviors or compulsions. People with OCD often feel driven to perform these rituals in order to alleviate their anxiety. It is a complex condition that affects individuals differently, but it generally leads to significant distress and interference in daily life.
Obsessions And Compulsions
Obsessions in OCD are intrusive, distressing thoughts or urges that cause anxiety and cannot be easily ignored or dismissed. They often revolve around themes such as contamination, fear of harming oneself or others, or a need for symmetry and order. Individuals feel compelled to engage in repetitive behaviors or mental acts as a response to their obsessions. Common compulsions include excessive handwashing, checking, counting, or organizing items in a specific way.
Medication And Therapy
The standard approach for treating OCD usually includes a blend of medication and therapy. The most commonly prescribed medications for OCD are selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), which can help reduce the frequency and intensity of obsessive thoughts and compulsive behaviors. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), particularly exposure and response prevention (ERP), is considered the most effective form of therapy for treating OCD. ERP involves gradually confronting feared situations and refraining from performing compulsive rituals, which helps individuals learn to tolerate anxiety and resist the urge to engage in compulsions.
Post-traumatic Stress Disorder (ptsd)
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is a type of anxiety disorder that can develop after an individual experiences a traumatic event, such as warfare, serious injury, sexual assault, or natural disasters. PTSD symptoms might encompass flashbacks, nightmares, intense anxiety, and persistent, uncontrollable thoughts related to the traumatic event. While the condition can be debilitating, there are various trauma-informed care strategies and treatments available to help individuals manage and overcome the challenges posed by PTSD.
Trauma Triggers
Individuals with PTSD may experience trauma triggers that can lead to intense emotional and physical reactions. These triggers can be associated with certain sounds, smells, or visual cues that remind the individual of the traumatic event. Recognizing and avoiding potential trauma triggers is an essential aspect of managing PTSD symptoms and reducing the risk of re-traumatization.
Trauma-informed Care
Trauma-informed care is an approach that emphasizes the understanding of the widespread impact of trauma and focuses on creating an environment that is sensitive to the needs of trauma survivors. This type of care encourages individuals to feel safe, welcomed, and understood, thus playing a crucial role in supporting individuals with PTSD.
Frequently Asked Questions For What Are The 6 Types Of Anxiety Disorders
What Are The 6 Types Of Anxiety Disorders?
Anxiety disorders include generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, specific phobias, agoraphobia, and separation anxiety disorder. Each type has its own unique symptoms and triggers, affecting individuals in different ways.
How Do I Know If I Have An Anxiety Disorder?
If you experience persistent and excessive worry, fear, or uneasiness that interferes with daily activities, relationships, or work, you may have an anxiety disorder. Other symptoms include restlessness, irritability, muscle tension, and difficulty concentrating. Consulting a medical professional for an accurate diagnosis is crucial.
Can Anxiety Disorders Be Effectively Treated?
Yes, anxiety disorders can be effectively treated through various methods such as therapy, medication, lifestyle changes, and self-help strategies. Seeking professional help, practicing relaxation techniques, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can significantly alleviate symptoms and improve one’s quality of life.
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of anxiety disorders is crucial for identifying and seeking appropriate help. By recognizing the specific symptoms and characteristics of each disorder, individuals can better navigate their mental health journey. With the right support and knowledge, it is possible to manage and alleviate the impact of anxiety in our daily lives.




Leave a Reply